× close
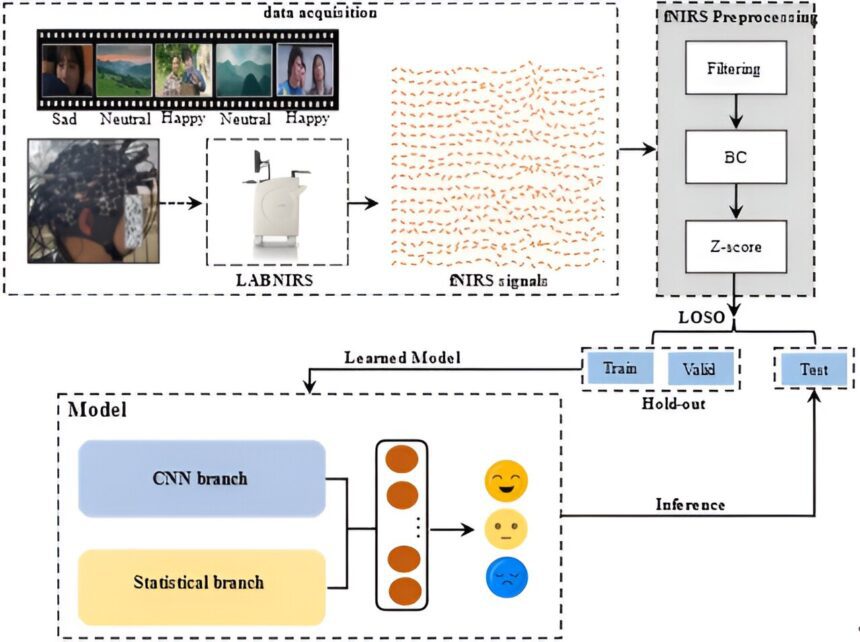
Cross-subject emotion recognition framework based on fNIRS, including data collection, data partitioning, model training and evaluation. Credit: Cyborg and bionic systems
Emotion recognition based on neural signals is leading the revolution in affective science. By analyzing brain activity, we can glimpse the secrets of the human inner world. This technology not only helps understand the nature of emotions, but also offers new possibilities in the field of mental health. Recognizing emotions using neural signals will be crucial to combat anxiety, depression or improve emotional intelligence. This allows us to understand how emotions affect our lives and our choices.
Previous approaches to emotion recognition mainly depended on sources such as questionnaires, facial expressions, voice, etc. These approaches suffer from problems such as high subjectivity and susceptibility to disruption. With advances and refinements in brain imaging technology, researchers can use these methods to measure neural activity signals without harming the brain during emotion triggering processes, allowing emotion types to be distinguished by neural activity traits.
Among them, functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is a novel non-invasive neuronal imaging technique, which is not only resistant to motion artifacts but also has high spatial resolution. A Chinese research group conducted a cross-subject emotion recognition study based on fNIRS signals and obtained high decoding performance, promoting the development of an affective brain-computer interface.
They published their recommendations in Cyborg and bionic systems.
“Cross-subject emotion recognition based on fNIRS has important prospects and significance. fNIRS technology is non-invasive, easy to use, and can measure brain activity. This helps us understand the emotional experiences of different people and offers new possibilities in the field of mental health. Through multi-subject studies, we can establish emotional patterns and identify the emotional characteristics of different groups of people. »
“This will contribute to personalized treatment, emotion regulation and psychological assistance. Cross-subject emotion recognition based on fNIRS provides us with a deeper and more comprehensive way to understand emotions and promotes the development of science emotional,” said the corresponding author. Xiaopeng Si, Associate Professor at the Academy of Medical Engineering and Translational Medicine, Tianjin University.
“By designing an emotion induction experiment with Chinese videos as natural stimuli and constructing an fNIRS emotion recognition database, we laid the foundation for exploring a new type of BCI for recognition of inter-subject emotions based on fNIRS”, Si and co-author He” said Huang.
Additionally, Si and Huang et al. introduced deep learning technology in this work, which significantly improved the emotion decoding performance. “Based on the characteristics of fNIRS signal data, a double branch common network (DBJNet) was specially constructed. The experimental results show that the model can be generalized to new subjects and has excellent inter-subject results . recognition of emotions performance,” said Si and his co-author He Huang.
More information:
Xiaopeng Si et al, Cross-subject emotion recognition brain-computer interface based on fNIRS and DBJNet, Cyborg and bionic systems (2023). DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0045
Journal information:
Cyborg and bionic systems
Provided by Beijing Institute of Technology Press Co.